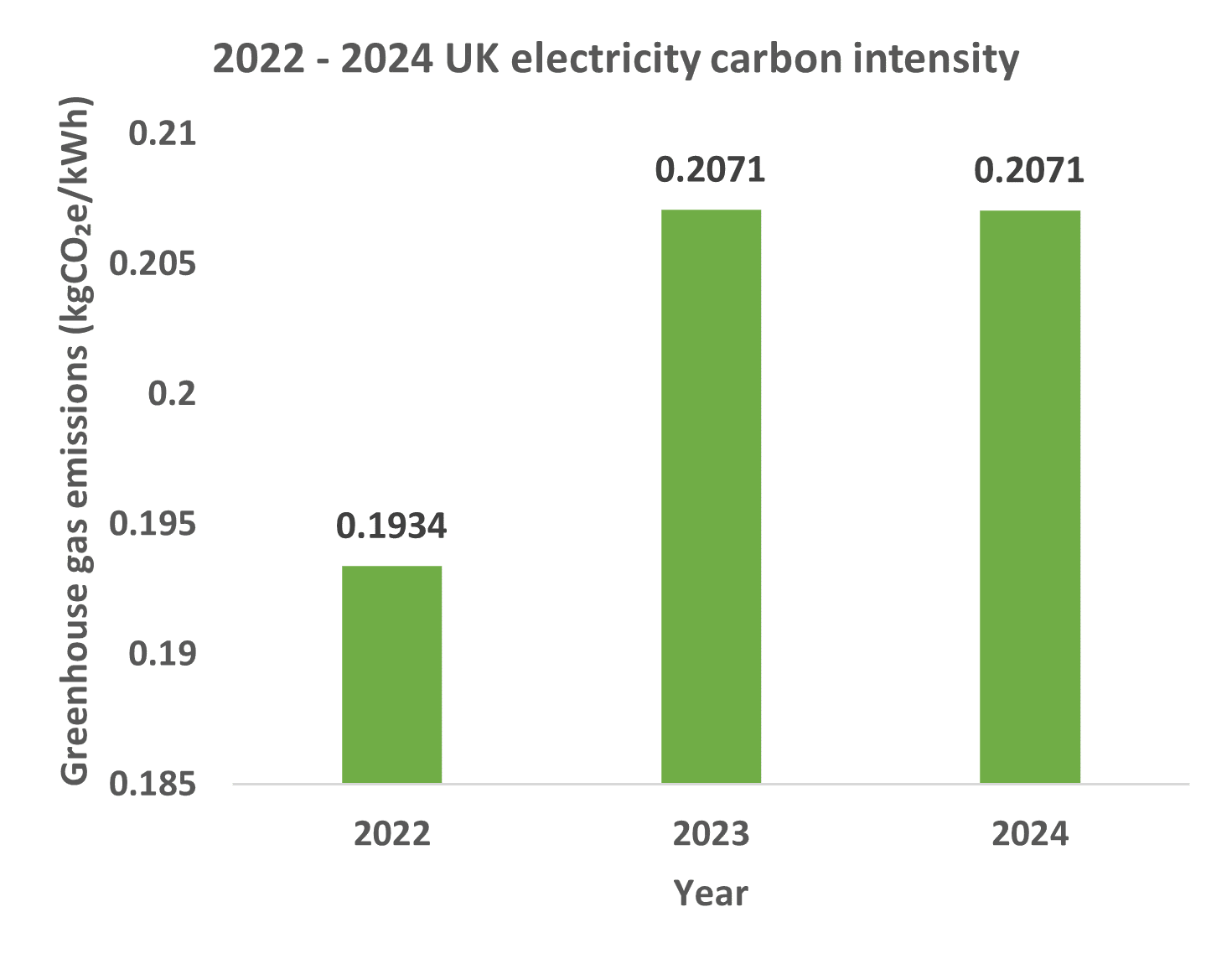News
Desnz 2024 Emissions Factors Released
The UK Department for Energy Security and Net Zero (Desnz) have just released the 2024 edition of conversion factors for calculating greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. These are also commonly known as the Defra GHG factors.
The factors cover emissions from a wide range of activities including energy, transportation, water and waste disposal.
Significant changes this year include updates to the plug-in hybrid electric vehicle (PHEV) factors to reflect real world performance and changes to material carbon factors with the latest available data.
What’s changed?
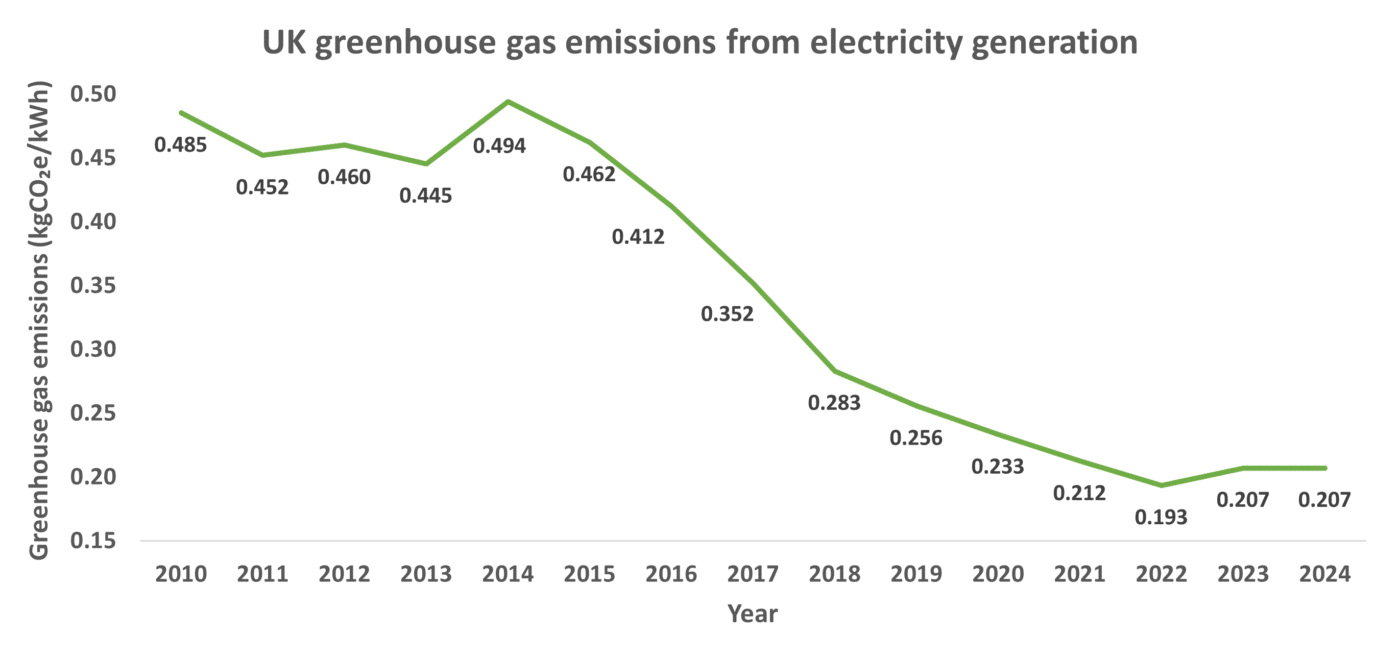
Below you can see the Scope 2 emissions of the UK’s electricity generation over time from the annual Desnz factors, showing a gradual decline in carbon intensity over time as renewables enter the UK’s electricity mix and the use of coal is phased out.
The results below exclude the well-to-tank (fuel production) and transmission and distribution impacts associated with electricity generation and transport.
The carbon intensity of the UK’s Scope 2 electricity generation has remained similar to the previous year, where it had increased by 7.1% from the 2022 factor. This was likely due to an increase in the use of coal and natural gas in the preceding year as fuel shortages became apparent. This was the first increase in the carbon intensity of the UK’s grid since 2014.
You can see our discussion on the likely future changes to the UK grid carbon impact here, where we discuss the Future Energy Scenarios from the National Grid and what this means for operational carbon reductions.
To access the 2024 Desnz factors, please visit here.
Need help?
Calculating an accurate and meaningful trend in your greenhouse gas emissions is essential for effective carbon and environmental management.
If you need any help in effectively utilising emissions factors, or are interested in understanding your business’ carbon footprint, you can get in touch with us here, or view our carbon footprinting services.
Featured image provided royalty free from Pexels