Carbon Footprint, Energy, News, Sustainability
Carbon Footprint of UK Electricity 2018
Decarbonising the UK Electricity Supply
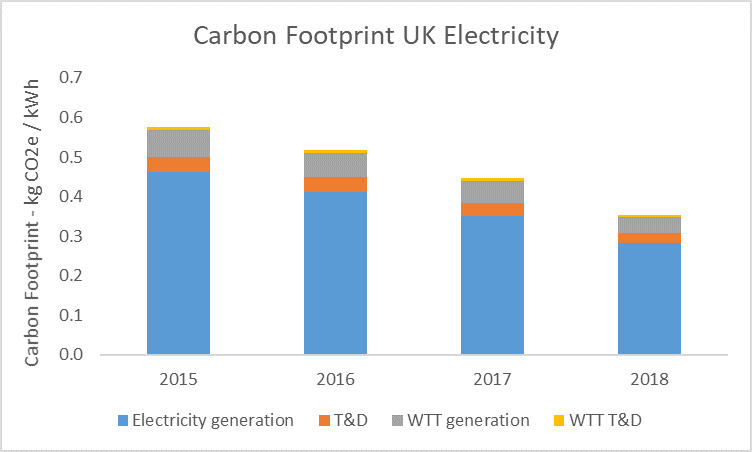
The emissions factor for electricity breaks down as:
- Electricity generation: These are the emissions directly at the power station, e.g. from burning natural gas, coal, and other fossil fuels.
- Transmission and distribution (T&D): The losses in the transmission and distribution network, e.g. cables and sub-stations.
- Well to tank (WTT) of fuel generation: The WTT emissions are the upstream emissions of fuel extraction, processing and transport.
- Well to tank of transmission and distribution: This accounts for the fuel extraction, processing and transport emissions of the energy lost through the distribution network.
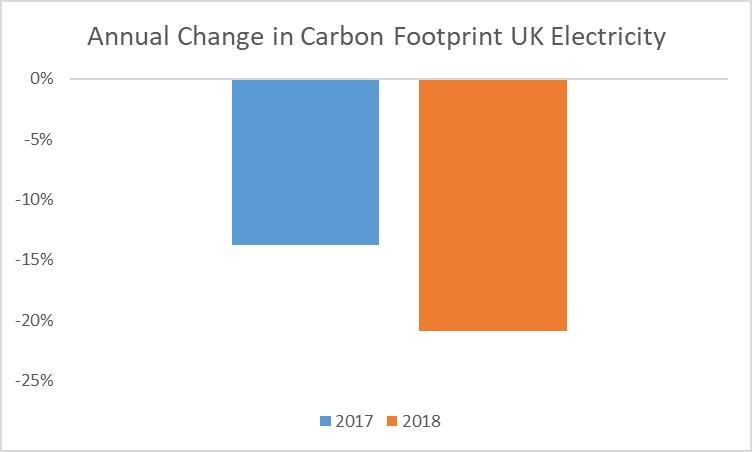
In the period of 1 year, the UK’s carbon footprint of a unit of electricity reduced by almost 21%, a particularly impressive year on year reduction.
Likewise, the reduction from 2016 to 2017 was a 14% reduction in the carbon footprint of a unit of electricity. These are impressive reductions and will surely help the UK to meet the legally binding GHG emission reduction targets. However, can such impressive carbon reductions be sustained when the 2019 factors come out?
If you like this post please consider sharing it on social media using the buttons below or signing up to our newsletter.
Key Reference:
The UK’s GHG emission factors for company reporting 2018 can be downloaded at the Government’s website, https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/greenhouse-gas-reporting-conversion-factors-2018